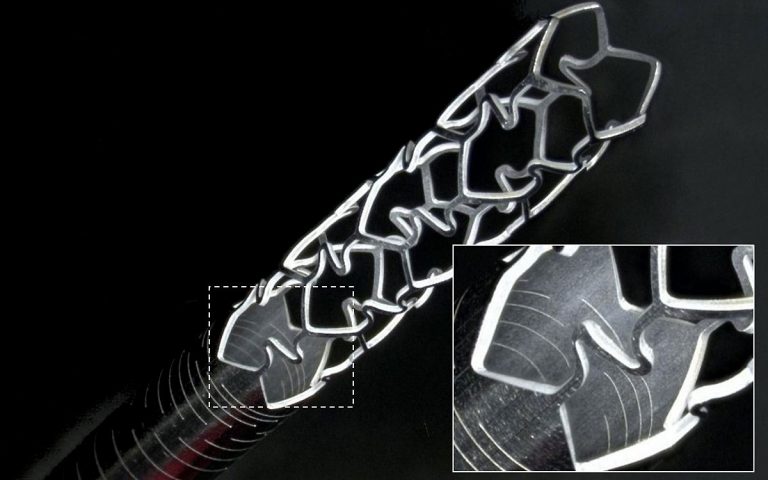
A stent is a tiny wire mesh or precisely cut tube inserted into a narrowed or blocked blood vessel. Stents help to treat approximately two million people every year. Cardiovascular stents have improved the lives of millions of patients. Nearly all coronary angioplasty procedures performed use stents. Heart stent technology has evolved a lot over the past 20 years and is continually advancing. Cutting stents with lasers is the most common choice for medical equipment manufacturers.
Stents save lives. Placed in blood vessels they keep the passageway open. Nowadays stents are manufactured from various metallic alloys (stainless steel, tantalum, cobalt–chromium, platinum–chromium, nitinol) and plastic (polyethylene, teflon, polylactide) or other biocompatible materials. The challenge of manufacturing various materials with micrometer precision makes femtosecond lasers perfect tools for various stent production.
Femtosecond lasers PHAROS or CARBIDE are the most common choice for stent manufacturers. It is possible to process both metallic and plastic stents using lasers equipped with a harmonics module. Moreover, femtosecond lasers eliminate costly post-processing and cleaning steps.
- 190 fs – 20 ps 连续可调脉宽
- 最大输出 1 mJ @ 120 W 或 2 mJ @ 80 W
- 单脉冲 – 2 MHz 重复频率
- POD 和 BiBurst 功能
- 高达 5 次谐波或可调谐扩展
- 风冷型号
- 紧凑的工业级设计
- 100 fs – 20 ps 连续可调脉宽
- 最大单脉冲能量 4 mJ
- 最小脉宽输出 < 100 fs
- POD 和 BiBurst 功能
- 高达 5 次谐波或可调谐扩展
- CEP 稳定或重复频率锁定
- 热稳定性和密封设计
Laser-Induced Superelasticity in NiTinol Stent Strut
C. A. Biffi, K. Mathivanan, and A. Tuissi, Shape Memory and Superelasticity 3 (4), 377-382 (2018).