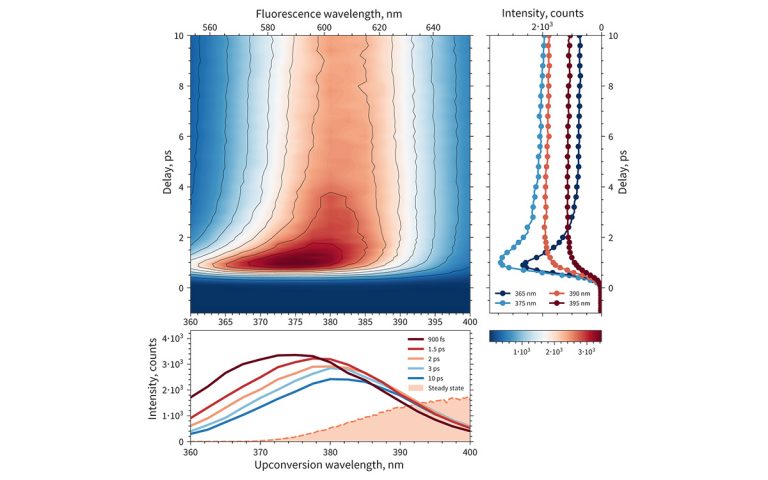
Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy carries information on the molecular processes in the excited state. A few techniques allow measuring fluorescence dynamics at different time scales using the same experimental setup:
- fluorescence upconversion,
- time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC),
- phosphorescence.
In the fluorescence upconversion experiment, the signal from the sample is mixed in a nonlinear crystal with a gating femtosecond pulse to achieve high temporal resolution, which is limited by the duration of the gate and pump pulses. For fluorescence decay times in the nanosecond to microsecond range, the instrument can be used in time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) mode to measure kinetic traces up to 5 μs. TCSPC technique can be further expanded to measure ultra-long fluorescence dynamics, for example, phosphorescence, lasting for milliseconds. The combination of these three time-resolved fluorescence techniques enables the measurement of spectrally-resolved fluorescence decay in the femtosecond to the millisecond range.
The HARPIA-TF is a time-resolved fluorescence measurement module that combines fluorescence upconversion and TCSPC techniques. With the use of a high repetition rate PHAROS or CARBIDE femtosecond laser, the fluorescence dynamics are measured while exciting the samples with pulse energies down to several nanojoules.
- 100 fs – 20 ps 连续可调脉宽
- 最大单脉冲能量 4 mJ
- 最小脉宽输出 < 100 fs
- POD 和 BiBurst 功能
- 高达 5 次谐波或可调谐扩展
- CEP 稳定或重复频率锁定
- 热稳定性和密封设计
- 190 fs – 20 ps 连续可调脉宽
- 最大输出 1 mJ @ 120 W 或 2 mJ @ 80 W
- 单脉冲 – 2 MHz 重复频率
- POD 和 BiBurst 功能
- 高达 5 次谐波或可调谐扩展
- 风冷型号
- 紧凑的工业级设计
- 190 nm – 16000 nm 可调波长
- 满足所有需求的高能量和高功率型号
- 单脉冲 – 2 MHz 重复频率
- 最高泵浦功率 80 W
- 最大泵浦单脉冲能量 2 mJ
Dopamine Photochemical Behaviour under UV Irradiation
A. Falamaş, A. Petran, A. Hada, and A. Bende, International Journal of Molecular Sciences 10 (23), 5483 (2022).
Electron–Hole Binding Governs Carrier Transport in Halide Perovskite Nanocrystal Thin Films
M. F. Lichtenegger, J. Drewniok, A. Bornschlegl, C. Lampe, A. Singldinger, N. A. Henke, and A. S. Urban, ACS Nano (2022).
Intrachain photophysics of a donor–acceptor copolymer
H. Nho, W. Park, B. Lee, S. Kim, C. Yang, and O. Kwon, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 4 (24), 1982-1992 (2022).
Large π-Conjugated Metal–Organic Frameworks for Infrared-Light-Driven CO2 Reduction
J. Zeng, X. Wang, B. Xie, Q. Li, and X. Zhang, Journal of the American Chemical Society 3 (144), 1218-1231 (2022).
Novel Synthetic Dopamine Analogues: Carbon-13/Nitrogen-15 Isotopic Labeling and Fluorescence Properties
C. Lar, S. Radu, E. Gál, A. Fălămaş, J. Szücs‑Balázs, C. Filip, and A. Petran, Analytical Letters, 1-13 (2022).
Size-dependent spectroscopic insight into the steady-state and time-resolved optical properties of ZnO photocatalysts
A. Falamas, I. Marica, A. Popa, D. Toloman, S. Pruneanu, F. Pogacean, F. Nekvapil, T. D. Silipas, and M. Stefan, Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 145, 106644 (2022).
Ultrafast Excited-State Proton Transfer of a Cationic Superphotoacid in a Nanoscopic Water Pool
H. Nho, A. Adhikari, and O. Kwon, The Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2022).
Comparison of growth interruption and temperature variation impact on emission efficiency in blue InGaN/GaN MQWs
J. Mickevičius, K. Nomeika, M. Dmukauskas, A. Kadys, S. Nargelas, and R. Aleksiejūnas, Vacuum 183, 109871 (2021).
Double Charge Transfer Dominates in Carrier Localization in Low Bandgap Sites of Heterogeneous Lead Halide Perovskites
A. Fakharuddin, M. Franckevičius, A. Devižis, A. Gelžinis, J. Chmeliov, P. Heremans, and V. Gulbinas, Advanced Functional Materials 15 (31), 2010076 (2021).
Germanium-lead perovskite light-emitting diodes
D. Yang, G. Zhang, R. Lai, Y. Cheng, Y. Lian, M. Rao, D. Huo, D. Lan, B. Zhao, and D. Di, 1 (12) (2021).